Blockchain could be the key to effective tracking of carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. This solution could prove useful in a context of global warming. Energy systems are currently aiming for decarbonization. Promoting transparency will be key to ensuring that entities in the global supply chain comply with the new emissions standards. So the supply chain could have a role to play.
How do you measure a product’s environmental impact?
Take into account all stages of a product’s life cycle
There has been much debate about how to assess whether a product is truly sustainable. But is it enough to look at the emissions of the company that sells it to the end customer?
First, we need to assess a product’s impact at every stage of its life cycle. From the extraction of raw materials to the disposal or recycling process.
This measurement process is known as Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). It’s the calculation and evaluation of the various impacts that a product or project can have on environmental, social and economic aspects.
But after all, what is a product if not the result of all its production stages?

Blockchain “decomplexes” product tracing
The problem is that tracing all these production stages is difficult in a globalized world. This is because they are usually geographically dispersed, carried out by several different players or entities, often in several different facilities, and using several different technologies.
Globalization has considerably increased the complexity of supply chains. This complexity poses a number of challenges in terms of controlling and monitoring these impacts at every stage of the life cycle. The fact that companies often have a restricted view of their limits is also a factor.
Scope 3 emissions are difficult to measure, but must be taken into account.
The different emissions “scopes
In the context of global warming, analyzing the classification of carbon emissions is relevant. These carbon emissions can be evaluated in three categories, known as scopes:
Scope 1 carbon emissions are the direct result of sources owned or controlled by the company. Scope 2 emissions represent carbon emissions indirectly generated by energy purchased and consumed during production. Finally, scope 3 emissions are indirect emissions throughout the value chain of a product or company. Scope 3 carbon emissions also include the use of a product by the end consumer.
To find out more about scopes and how carbon emissions are classified, read our article on the subject.
The importance of measuring Scope 3 emissions
Scope 3 emissions are the most comprehensive measure of impact. Indeed, the latter can account for up to 75% of a product’s total emissions footprint. But they are also the most difficult to calculate.
Supply chain emissions require a high level of integration and coordination between its multiple networks.
Different entities must share the data needed to certify the sustainability of products and guarantee their traceability. This step is therefore essential. Anything that can be quantified is no longer a risk, but becomes a management issue.
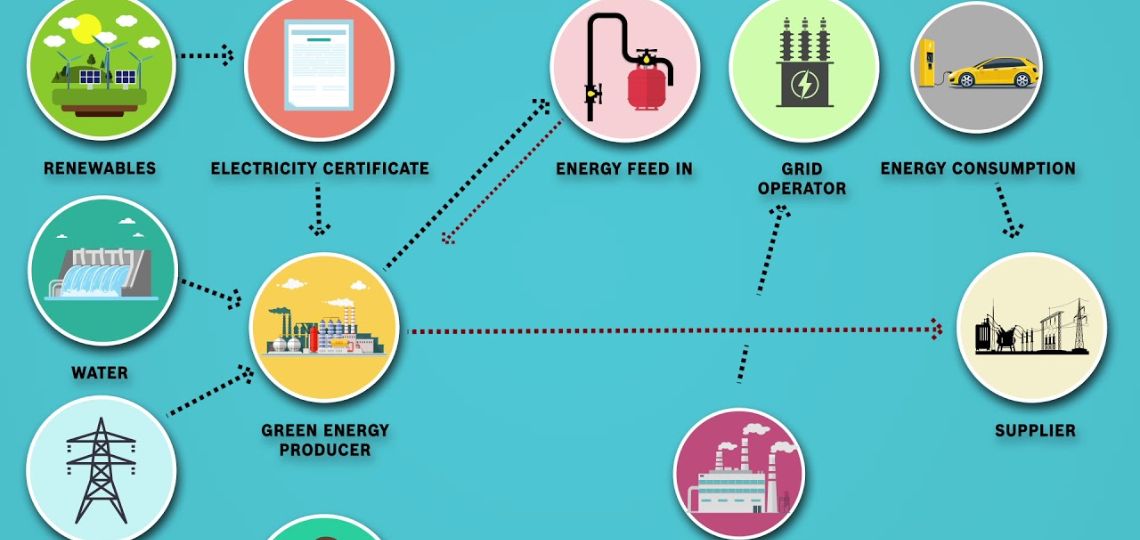
Traceability and data transparency are essential for monitoring emissions
Data sharing can have two main objectives: transparency and traceability. These terms are often confused, but they imply different objectives.
Improving transparency to get to know the players
Transparency aims to gather high-level information on supply chains. This is achieved by mapping the value chain network in terms of supplier names, facility locations, product attributes and certification.
The main aim of improving transparency is to make it clearer which paths a product follows along supply chains. This makes it possible to gather information on the players involved at every stage.
Improved traceability for better impact measurement
Traceability, on the other hand, requires a higher degree of granularity in the information shared. This information can be, for example, the dates and places of purchase of product components, specific item properties or more operational information.
Increased traceability enables more precise measurement of impacts at every stage of the supply chain. It enables data-driven strategies to be developed and sustainability claims to be verified.
Blockchain can digitally certify carbon emissions footprint
How to track carbon emissions with blockchain
The blockchain’s large distributed ledger can record consumption data from different entities in different locations in real time. We can then calculate the carbon intensity of this consumption.
Finally, we can automatically assign a certificate supplied with the transferred energy. This certificate proves where and when the energy was produced.
Blockchain makes it possible to certify energy emissions
Blockchain can improve the energy system by ensuring trust, traceability and auditability. A digital process called “electricity tokenization” makes this possible. Through this process, units of electricity become digital goods or assets. This enables automatic generation of time-stamped certificates. Transfer and tracking of ownership (based on cryptographic evidence) are also possible.
This process also ensures that certificates are sold only once, and that there is no double counting. Auditors can trace electricity consumed in the supply chain to any stage in its lifecycle.
It’s the only real way to slow global warming throughout the supply chain, and to be totally ecological at all times.






















