Researchers from the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have announced the development of the first uranium-based rechargeable battery, utilising this chemical element as an active material for energy storage. The project, led by the NXR Development Centre of the Nuclear Science Research Institute, aims to transform Japan’s stockpiled depleted uranium into a useful energy asset. A patent was filed on 29 November 2024 under number JP2024-209096.
A storage solution derived from nuclear by-products
Depleted uranium, a by-product of nuclear fuel enrichment, cannot be used in current light-water nuclear reactors. Japan currently stores approximately 16,000 tonnes of this material. Since the early 2000s, research had suggested the potential use of depleted uranium as an active battery material, but no conclusive experimental data had been published until now.
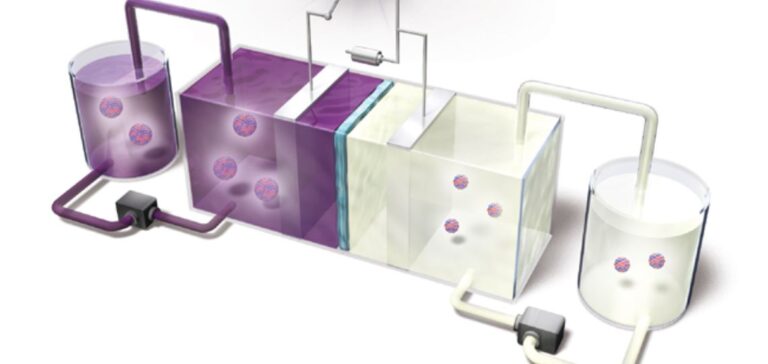
The developed battery uses uranium as the negative electrode and iron as the positive electrode. The prototype achieved a voltage of 1.3 volts, close to that of standard alkaline batteries. Tested over ten charge-discharge cycles, the battery demonstrated consistent functional stability, indicating promising cycling potential for future applications.
Towards integration into renewable energy grids
Instabilities linked to renewable sources such as solar and wind energy require storage systems to stabilise electricity distribution. The uranium-based battery could meet this need if its capacity is increased, notably through the development of redox flow systems. These systems include circulating electrolytes and specialised electrodes to enhance autonomy and storage capacity.
This approach reflects the rising demand for innovative storage technologies capable of supporting the growing deployment of renewable energy. Using an already available and previously unutilised resource presents a dual industrial benefit: reducing depleted uranium stockpiles and securing energy supply during transitional periods.
A research programme with targeted industrial outlooks
The uranium battery project was led by Assistant Principal Researcher Kazuki Ouchi, Researcher Katsuhiro Ueno, and Senior Principal Researcher Masayuki Watanabe, all members of the Special Team for Battery Energy Storage within the JAEA. The next steps involve scaling the system to pilot level and optimising cells for industrial use.
The results obtained at this stage do not yet allow for immediate commercialisation, but represent a notable technical step forward in the valorisation of nuclear by-products. The industrial feasibility of this technology will depend on progress in safety, long-term cycling performance, and the cost of integration into existing energy networks.