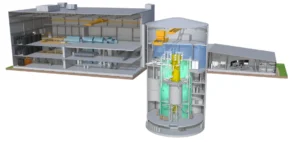
Malaysia’s Ministry of Energy Transition and Water Transformation (PETRA) officially announced on August 2 the launch of a feasibility study on the potential integration of civil nuclear energy into the country’s energy mix. This initiative is part of the 13th Malaysia Plan (2026–2030), presented by Prime Minister Datuk Seri Anwar Ibrahim on July 31. The primary objective is to determine whether nuclear energy can meet the country’s long-term energy security needs while supporting diversification and structural transformation of the electricity system.
The project is led by MyPOWER Corporation, a special purpose entity under PETRA, and follows a roadmap developed in accordance with recommendations from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The study encompasses several dimensions, including regulatory frameworks, infrastructure analysis, human resource development, and institutional coordination across ministries and agencies. The government emphasized that no decision has yet been made regarding the technology, capacity, or timeline for potential nuclear deployment.
Targeted Regions and Grid Constraints
According to initial information from authorities, the feasibility study will focus primarily on Peninsular Malaysia and Sabah. These regions face specific challenges related to the availability and stability of renewable electricity sources. In Sabah, energy generation mainly relies on hydro and solar power, both of which have limited capacity and are heavily dependent on battery storage systems.
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Energy Transition Datuk Seri Fadillah Yusof stated during the 5th International Green Build Conference in Petaling Jaya that, despite the presence of local biomass and biogas resources, these remain insufficient to ensure regional energy autonomy. In this context, a centralized and stable energy source such as nuclear is being evaluated as a strategic option.
Regulatory Framework and Public Acceptance
In parallel with technical analysis, the government is undertaking a comprehensive review of the existing legal framework. This includes identifying necessary regulatory amendments in line with international standards for nuclear safety, security, and non-proliferation. The adopted methodology is based on the IAEA Milestones Approach, which serves as a benchmark for countries in the preliminary stages of nuclear program development.
The study also emphasizes the importance of human capital development, both in terms of technical expertise and regulatory enforcement. The ministry also plans public engagement initiatives to strengthen societal acceptance of a potential nuclear program. At this stage, the focus remains on the thoroughness of technical and regulatory assessments, with no commitment yet to actual implementation of a nuclear project.