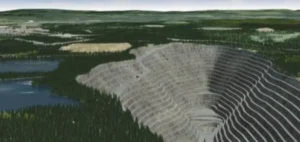
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) suspended operations at its Jianxiawo lithium mine in Jiangxi province on August 9, triggering an immediate 8% surge in lithium carbonate prices on the Chinese market. The futures contract on the Guangzhou Futures Exchange reached 81,000 yuan per metric ton, hitting the daily trading limit. This suspension comes after the facility’s mining permit expired, according to official statements from the company on its investor interaction platform. The mine produces approximately 65,000 tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent annually, representing 3% of projected global supply for 2025.
Economic Impact and Regulatory Context
Production costs at Jianxiawo amount to approximately 100,000 yuan per tonne, significantly exceeding the current market price of 70,000 yuan for battery-grade lithium carbonate. This economic disparity has placed the operation in a loss-making position for several months. The Yichun Natural Resources Bureau identified compliance issues at eight mines in the region, requiring submission of reserve verification reports before September 30, 2025. This regulatory action falls under the new Mineral Resources Law that came into effect in July, aimed at reducing overcapacity in China’s lithium sector. Tibet Zangge Mining also suspended its lithium carbonate production in Haixi Prefecture, Qinghai on July 17, in accordance with local government requirements.
Platts data indicates battery-grade lithium carbonate traded at 80,000 yuan per metric ton on a delivered duty-paid China basis on August 11, up 8,000 yuan from the previous day and 16,000 yuan from the previous month. This assessment represents the highest level observed since November 25, 2024. Lithium hydroxide also recorded similar price movements, reflecting tensions across the entire supply chain.
Global Supply Chain Repercussions
Jianxiawo’s production supplies cathode material for approximately 500,000 electric vehicle batteries annually. Major automakers including Tesla, BYD, and NIO source battery cells containing lithium from Jiangxi. Procurement teams are activating alternative arrangements with Australian spodumene producers and Chilean brine operations, but shipping lead times create immediate shortages. CATL holds 30 to 45 days of lithium carbonate inventory in its battery plants, insufficient if the suspension extends beyond September.
Fastmarkets analysts project an oversupply of only 10,000 tonnes in 2025, shifting to a deficit of 1,500 tonnes in 2026. Global lithium demand is expected to exceed 1.4 million metric tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent in 2025. The global electric vehicle battery market is expected to reach $251.33 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate of 9.6%.
CATL Financial Performance and Market Outlook
CATL recorded a net profit of 50.7 billion yuan in 2024, up 15% despite a 9.7% decline in revenue to 362 billion yuan. This revenue decline is explained by price adjustments following the drop in raw material costs. The company maintains a 36.8% global market share in electric vehicle batteries. Energy storage revenue now represents 15.83% of total sales, up from 14.94% in 2023, illustrating business diversification beyond the automotive sector.
China controls 65% of global lithium processing capacity, consolidating its dominant role despite lacking significant domestic reserves. Chinese investments in mining projects in Africa, Australia, and South America could multiply African production by 30 by 2027. Western automakers are developing alternative supply chains but remain dependent on Chinese processing for critical battery components.
Battery-grade lithium carbonate prices are expected to range between $9,000 and $12,000 per tonne according to analyst projections. The Jianxiawo suspension could represent the beginning of a broader realignment in Chinese lithium production, with several mines in the Yichun region under increased regulatory scrutiny.