The Nordic electricity markets, with Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden leading the way in the integration of renewable energies, have taken the lead in the race for energy transition. With its emphasis on renewables and abundant system flexibility, the region is undoubtedly decades ahead of other markets and will play a central role in Europe’s “net zero” ambitions.
Nordic Electricity Markets ahead of their time
Scandinavia and Finland lead the world in the integration of renewable energies. The Nordic countries boast some of the highest levels of renewable energy in the world. Historically, electricity prices are also the lowest in Europe. Hydroelectricity currently predominates.
In Norway, for example, the supply of renewable energy is close to 100%, with 80% coming from highly flexible hydroelectric power. Denmark, meanwhile, has the world’s highest penetration rate ofwind and solar power, thanks to early political guidance. Finally, Sweden and Finland both boast high levels of renewable energy integration, complemented by nuclear power.
Wind and solar ahead of hydropower by 2038
The abundance of resources means that wind power will continue to develop in the region. Wind and solar together will overtake hydropower as the dominant energy source in the Nordic countries by 2038. Hydropower will continue to offer the necessary flexibility, but it will be part of a more dynamic whole.
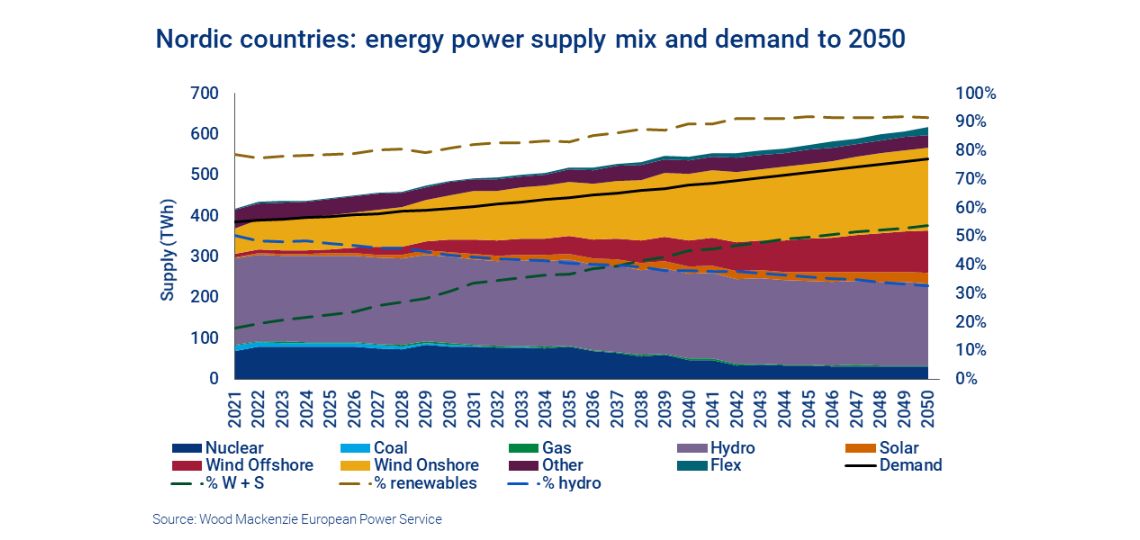
Demand set to outstrip supply
The Nordic countries’ energy mix will have to cope with growing demand. Wood Mackenzie forecasts a 30% increase – mainly due to electric vehicles, electrification of heating, data centers and battery gigafactories – from 390 TWh today to 540 TWh in 2050.
Growth will be driven mainly by onshore and offshore wind power, with solar power also contributing. Hydropower will remain relatively stable in absolute terms, but its share of supply will be reduced. The contribution from nuclear power will also decrease, as Sweden completes its nuclear phase-out. Leaving only Finnish power plants in operation.
Nordic countries divided between net importers and exporters
Overall, Norway and Sweden tend to export a surplus of energy, while Finland and Denmark are net importers. However, resource distribution and demand density vary across the region, not only between countries, but also between bidding zones within them.
As a result, the Nordic electricity market is defined by significant electricity transfers, both within the region and beyond, made possible by high levels of interconnection. As renewable energy penetration continues to grow, not only in the Nordic countries but also in continental Europe and the UK, the business case and system needs for further interconnection will crystallize. This is an essential component of a successful energy transition in the Nordic countries and Europe.






















