Savannah Resources has announced a further delay to the start of production at its lithium mine located in Barroso, northern Portugal. Originally scheduled for 2027, production is now expected to begin in 2028. This delay results from a postponement in securing a key land easement, which is now anticipated in the fourth quarter of 2025 following Portugal’s municipal elections set for October 12.
Second delay in under a year
The London-listed company had already postponed the project from 2026 to 2027, citing a change in government in September 2024. The latest adjustment also pushes back the delivery of the definitive feasibility study, now expected in the first half of 2026 instead of late 2025.
The project was temporarily halted in February 2025 due to a land rights dispute with local opposition groups. On August 22, a United Nations committee concluded that Portugal had failed to uphold citizens’ rights to environmental information and participation in the permitting process.
An asset aligned with EU priorities
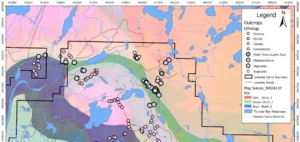
Despite the challenges, the Barroso project retains its strategic status under the European Union’s Critical Raw Materials Act. Considered Europe’s largest spodumene deposit, the project is one of 47 critical initiatives supported by the European Commission. Currently, no lithium production sites are operational within the EU, although five projects are in development phases.
The current drilling programme was completed in July, with assay results released in August. Savannah expects to announce updated resource estimates in September. A 2023 scoping study projected total output of 2.6 mn tonnes of spodumene concentrate at 5.5% Li2O over a 14-year mine life, with average annual output of 191,000 tonnes.
Financing prospects under discussion
The project has already attracted financing interest. In December 2024, Savannah announced receipt of a non-binding letter of interest from German agency Euler Hermes, confirming preliminary eligibility for an untied loan of up to $270 mn.
Rising lithium prices may further support the project’s viability. On September 3, battery-grade lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide were both assessed at $9,500/tonne CIF Europe, marking a 15% increase over the previous month.