GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy and Finnish energy group Fortum have concluded an initial agreement to collaborate on pre-licensing and site adaptation aspects for hosting BWRX-300 (Boiling Water Reactor X-300) small modular reactors. This cooperation specifically targets the Finnish and Swedish markets, where Fortum is evaluating the technological and commercial conditions required for possible deployment in the next decade. GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy has previously collaborated with various Nordic nuclear stakeholders, thus possessing significant experience in the region. The partnership forms part of a broader dynamic aiming to strengthen energy capacity amid growing electricity demand.
A structured approach open to various partners
Fortum, 51.26% owned by the Finnish state, launched a feasibility study in October 2022 focusing on the economic, technical, and societal prerequisites for new nuclear projects in Scandinavia. Following a detailed assessment of several nuclear technologies, the company finally selected three distinct technologies in March, including the BWRX-300. Other chosen technologies include the conventional AP1000 reactors from Westinghouse-Hyundai and the EPR (European Pressurized Reactor) from EDF.
Nicole Holmes, Chief Commercial Officer of GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy, stated: “After carefully studying various aspects of SMR (Small Modular Reactor) technologies over the past two years, Fortum concluded that the BWRX-300 constituted a potential solution suited to its Finnish and Swedish markets.”
Nuclear energy expansion in Scandinavia
Fortum currently operates several significant nuclear facilities, notably the Loviisa plant in Finland, consisting of two VVER-440 type reactors. This plant represents over 10% of electricity production in Finland. The company also holds stakes in the Olkiluoto nuclear plants in Finland, as well as Forsmark and Oskarshamn in Sweden.
The company recently applied to Finnish authorities for an extension of the operating licenses of the two Loviisa plant units until 2050. These licenses will expire in 2027 and 2030 respectively. Markus Rauramo, Fortum’s President and CEO, previously indicated that rising electricity demand in the Nordic countries would necessitate significant investments in new production sources.
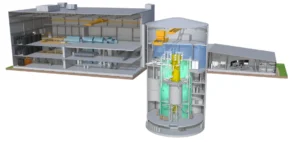
The BWRX-300, a technology under international development
The BWRX-300 is a 300-megawatt modular reactor intended for deployment in various countries. Last May, Canada already announced a project involving the installation of four units at the Darlington site in Ontario. Other markets are also examining the potential use of this technology in the coming years. GE Vernova Hitachi Nuclear Energy and Fortum are relying on their current cooperation to establish the groundwork necessary for eventual deployment in Scandinavia.