The United States Department of Energy (DOE) announced the creation of a consortium bringing together nuclear industry players to develop domestic enriched uranium production. This initiative is based on the use of the Defense Production Act (DPA), a legal framework allowing voluntary agreements with companies to secure resources deemed critical for national security. The stated goal is to establish a reliable nuclear fuel supply chain, including low-enriched uranium (LEU) and high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU).
Reducing external dependence
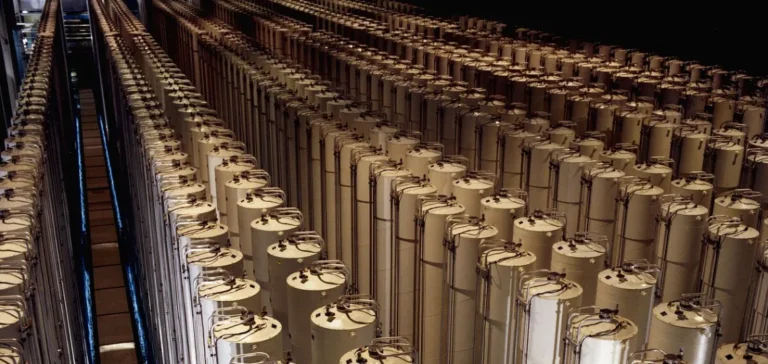
The United States still relies heavily on foreign sources for uranium conversion and enrichment. Russia has long been a major supplier of nuclear fuel, particularly HALEU, enriched up to 20% uranium-235, which is essential for the development of next-generation reactors. A federal law now provides for the end of Russian enriched uranium imports starting in 2027, increasing pressure on US and European industrial capacity.
A coordinated mechanism
The use of the DPA gives companies participating in the consortium protection from antitrust regulations, as long as their actions fall within national energy security priorities. The DOE specified that the selection of consortium members would be finalized in the coming weeks, with a first meeting scheduled for October. Selected companies will have to demonstrate concrete progress in establishing supply capacities for LEU and HALEU.
Industrial capacity and public funding
Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, several Western nuclear fuel cycle companies have announced expansion projects in the United States and Europe. The US government has already redirected more than USD 2.7 billion in federal funding to support the development of enrichment facilities. The DOE, however, considers these measures insufficient to ensure energy autonomy, justifying the launch of this new coordination tool.
Precedents and implications
The DPA had previously been used to oversee industrial cooperation during the 2020 pandemic, particularly in the health sector to secure access to critical equipment. By applying it now to nuclear energy, US authorities aim to prevent a supply shortfall that could impact electricity generation, as demand grows with the expansion of data centers and low-carbon electricity needs. This approach raises questions about how quickly industry players will be able to build new capacity under a tight timeline.