Fermi America has signed an agreement with Energy Transfer to secure a firm natural gas supply for powering Phase One of its HyperGrid energy campus, dedicated to artificial intelligence, near Amarillo, Texas.
A two-year project aims to identify areas in Texas suitable for natural hydrogen exploitation, despite challenges related to infrastructure, public policy and economic viability.
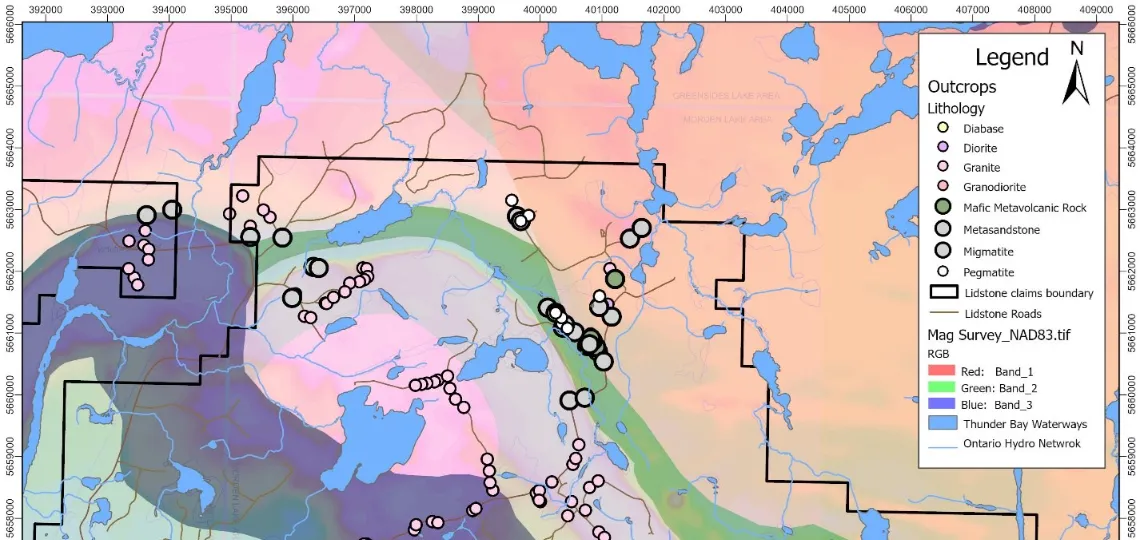
First Lithium Minerals begins a field programme at its Lidstone project, aiming to identify gold or base metal drilling targets in a historically underexplored greenstone belt.
Rockpoint Gas Storage priced its initial public offering at C$22 per share, raising C$704mn ($515mn) through the sale of 32 million shares, with an over-allotment option expanding the transaction to 36.8 million shares.
The European Investment Bank unlocks an unprecedented $250mn loan to support the construction of Costa Rica’s first electric rail system, in partnership with two regional financial institutions.
German wind turbine manufacturer Nordex secured 2,170 MW in new orders between July and September, bringing its total volume to 6.7 GW over nine months.
Faria Renewables a finalisé l’acquisition de deux projets éoliens d’une capacité cumulée de 30,8 MW, consolidant son portefeuille d’actifs en Grèce et poursuivant son expansion stratégique sur le marché national.
Google has signed a power purchase agreement with Eneco to supply its Belgian data centre with wind energy from three wind farms totalling 54 MW.
Italian group Dolomiti Energia secures €200mn loan from the European Investment Bank to finance wind farms and modernise power infrastructure in two strategic regions of the country.
Global progress on electricity access slowed in 2024, with only 11 million new connections, despite targeted efforts in parts of Africa and Asia.
Eni begins the transformation of its Priolo complex in Sicily with a 500,000-tonne biorefinery and a chemical plastic recycling plant, based on its proprietary Hoop® technology.
Norwegian-based Kyoto has launched a 56 MWh thermal storage system at KALL Ingredients in Hungary, designed to replace natural gas with renewable-based industrial heat.
An international audit led by the International Atomic Energy Agency confirms that Spain has fully addressed the recommendations made in 2018 regarding its nuclear waste management programme.
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development is reviewing a loan for a 100 MW photovoltaic project led by Qair in Tunisia, backed by a long-term power purchase agreement with the national utility.
An agreement was reached between Khartoum and Juba to protect key oil installations, as ongoing armed conflict continues to threaten crude flows vital to both economies.
Alnaft has signed two study agreements with Omani firm Petrogas E&P on the Touggourt and Berkine basins, aiming to update hydrocarbon potential in key oil-producing areas.
Gauss Fusion has released a full-scale plan for GIGA, its first commercial fusion power plant, amid Germany’s growing ambition to lead the future energy race.
Ferrari unveiled the chassis of its first electric vehicle, the Elettrica, while announcing a revision of its electrification targets, favouring thermal and hybrid powertrains for the coming decade.
Import quotas exhaustion and falling demand push Chinese independent refineries to sharply reduce Iranian crude volumes, affecting supply levels and putting downward pressure on prices.
Serbian oil company NIS, partially owned by Gazprom, faces newly enforced US sanctions after a nine-month reprieve, testing the country's fuel supply chain.
- Last news
CMSI launches a public consultation until 17 November to finalise a common mining standard designed to simplify industrial requirements and strengthen global adoption.
US nuclear technology firm NANO Nuclear Energy has secured $400mn through an oversubscribed private placement, raising its cash position to approximately $600mn to accelerate development of its KRONOS MMR™ microreactors.
Plug Power finalised a deal with an institutional investor to raise $370mn through the immediate exercise of warrants, with the possibility of securing an additional $1.4bn if new warrants are exercised.
Tailwater Capital secures $600mn in debt and $500mn in equity to recapitalise Producers Midstream II and support infrastructure development in the southern United States.
Air Liquide announces a $50mn investment to strengthen its hydrogen network on the US Gulf Coast, following long-term contracts signed with two major American refiners.
Nala Renewables strengthens its position in Finland with the acquisition of a battery energy storage portfolio exceeding 250 MW from Swiss developer Fu-Gen AG.
Developer Gwynt Glas enters development phase after signing a lease agreement with The Crown Estate, paving the way for a 1.5GW floating offshore wind project in Welsh waters.
From January 2026, the southern Polish city of Sosnowiec will power its municipal institutions entirely with renewable electricity under a public contract awarded to local provider Hekla Energy.
GOLDBECK SOLAR Polska has received the Final Operational Notification for its Zwartowo photovoltaic facility, marking a key regulatory milestone in the development of large-scale solar projects in Poland.
German group Uniper has entered into a long-term supply deal with Five Bioenergy for biomethane produced in Spain, with deliveries scheduled to begin in 2027.
An economic study reveals that Germany’s gas storage levels could prevent up to €25 billion in economic losses during a winter supply shock.
The main European automotive lobby is calling for looser 2030 and 2035 emission targets, promoting hybrids and carbon-neutral fuels.
Russian oil output moved closer to its OPEC+ allocation in September, with a steady rise confirmed by Deputy Prime Minister Alexander Novak.
Ambassadors of European Union member states have approved the transmission of a legislative proposal to phase out Russian fossil fuel imports by January 2028 to the Council of Ministers.
The State Duma has approved Russia’s formal withdrawal from a treaty signed with the United States on the elimination of military-grade plutonium, ending over two decades of strategic nuclear cooperation.
Amid rising energy costs and a surge in cheap imports, Ineos announces a 20% workforce reduction at its Hull acetyls site and urges urgent action against foreign competition.
Driven by the energy, heavy industry and power generation sectors, the global carbon capture and storage market could reach $6.6bn by 2034, supported by an annual growth rate of 5.8%.
Article 6 converts carbon credits into a compliance asset, driven by sovereign purchases, domestic markets, and sectoral schemes, with annual demand projected above 700 Mt and supply constrained by timelines, levies, and CA requirements.
Global demand for industrial gases will grow on the back of hydrogen expansion, carbon capture technologies, and advanced use in healthcare, electronics, and low-carbon fuel manufacturing.
Fuel shortages now affect Bamako, struck in turn by a jihadist blockade targeting petroleum flows from Ivorian and Senegalese ports, severely disrupting national logistics.