The new oil could be green hydrogen in Saudi Arabia. This energy is currently booming worldwide, seen as one of the solutions for achieving decarbonization objectives. Saudi Arabia is betting on this resource to create its new futuristic city: Neom.
New oil to power the city of Neom
The new city of Neom is to be built along the Red Sea, on the edge of the Saudi Arabian desert. The state has invested over $500 billion to develop a city based on advanced technologies that will accommodate a million people. Saudi Arabia is betting not on oil, but ongreen, carbon-neutralhydrogen to power this electricity-hungry project.
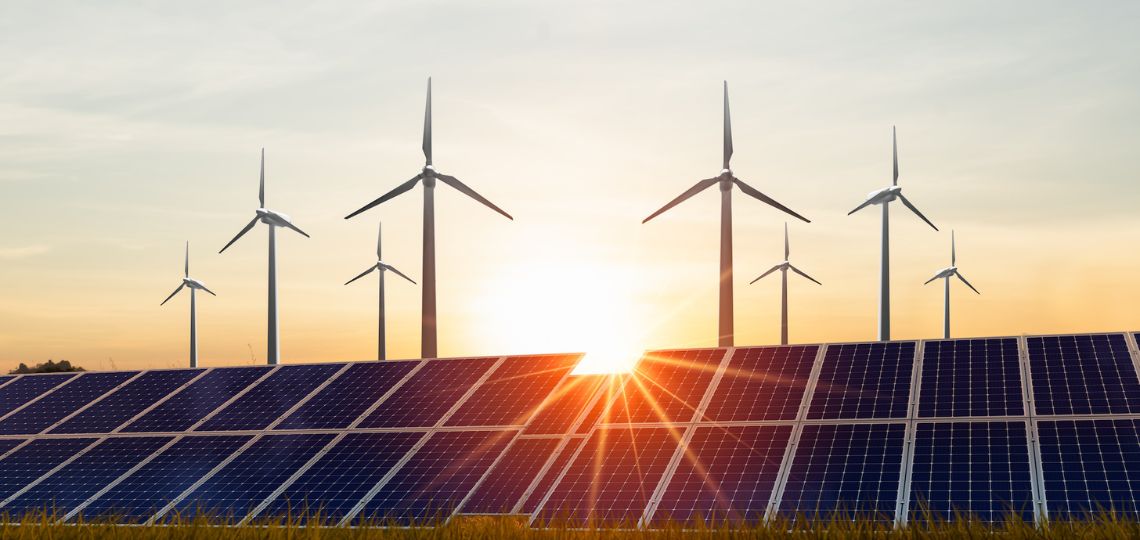

A new hydrogen plant to power Neom
The major American gas company, Air Products & Chemicals, announced that it had been building agreen hydrogen production plant in Saudi Arabia for four years as part of this project. The plant is powered by four gigawatts of electricity from wind and solar projects stretching across the desert. However, other projects are under study.
The Middle East currently has high-quality, low-cost wind and solar energy resources, such as the 300 MW Sakaka site. An opportunity for this new project, which could propel Saudi Arabia to the forefront of green hydrogen.
Koch Blank, head of the Rocky Mountain Institute’s Breakthrough Technology program, said:
“Saudi Arabia has ridiculously cheap renewable energy. The sun shines pretty reliably every day and the wind blows pretty reliably every night. It’s hard to beat.”
An important energy source for the energy transition
Green hydrogen could be an ideal energy source for energy-intensive industries such as concrete and steel manufacturing, as well as for sea and air transport. However, Airbus has highlighted the many storage problems associated with using this energy. He believes, however, thathydrogen could be flying airplanes by 2035. Roxana
Bekemohammadi, Executive Director of the Western States Hydrogen Alliance pointed out:
“Hydrogen fuel cells will power the future of emissions-free mobility in these heavy, hard-to-elect vehicle sectors. This fact is indisputable. ”
The new oil for a new green hydrogen “rush
Many countries are currently interested in this type of energy. The European Union and Germany, in particular, have allocated major investments to develop this energy on their territory.
An Australian consortium has also developedhydrogen businesses to Singapore, thanks to 1,743 large wind turbines and 30 square miles of solar panels. However, for the Asian Renewable Energy Hub, ammonia gas could be easier to export than hydrogen. Japan has also developed its own green hydrogen company at Fukushima.
Only the USA is lagging behind in this area, despite the development of hydrogen projects in Utah, California and Nevada. In fact, natural gas is still much cheaper and more attractive.
Hydrogen: A new oil, but still limited
At present,hydrogen production still relies on fossil fuels and is therefore not climate-friendly. Indeed, to power the electrolysis plants that separate water into hydrogen and oxygen, we’d need to massively expand renewable energy production. BloombergNEF estimates that producing enough green hydrogen to meet a quarter of the world’s energy needs would require an $11 billion investment in production and storage.
Hydrogen is also difficult to store and transport without a pipeline. Michael Liebreich, UK analyst at Bloomberg New Energy Finance said:
“It doesn’t exist in nature, so energy is needed to separate it. Its storage requires compression to 700 times atmospheric pressure, refrigeration to -253C… It carries a quarter of the energy per unit volume of natural gas… It can embrittle metal, it escapes through the smallest leaks and yes, it really is explosive”.
Finally, even if hydrogen appears to have great potential as a substitute for oil, its use remains limited by a number of obstacles, not least production costs.






















